Tag Archive for MySQL Cluster
Doxygen output for MySQL Cluster NDB API & MGM API
A new page has been added to this site: NDB API Docs which presents the information from the header files for both the NDB API and the NDB Management API.
The material has been generated using doxygen and will be refreshed shortly after any new major, minor or maintenance release is made generally available (starting from MySQL Cluster 7.0.6).
Tweet
New White Papers on deploying FreeRADIUS on MySQL Cluster
Before a client can start to access and consume services on a network, they must first be Authenticated to the network and then Authorized to use the services they are entitled too. Their consumption of network resources then needs to be captured via the Accounting processes. Collectively, Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) is a cornerstone of today’s network security, management and in many cases, monetization. RADIUS is a standard protocol to implement this AAA service.
As these networks grow, limitations can occur which add administrative overhead, inhibit flexible scaling and impact the timely synchronization of data across the AAA environment.
Using MySQL Cluster as the data store for a RADIUS server makes a lot of sense as it brings with it all of the standard MySQL Cluster benefits such as real-time response times, scalability, high availability and geographic redundancy.
Two new white papers have been produced to explain how MySQL Cluster can be used as the fault-tolerant, real-time, scalable data store for FreeRADIUS (a leading, open-source RADIUS server):
- Delivering Massively Scalable & Highly Available Authentication Services: a business white paper explaining the benefits to be gained by using MySQL Cluster as the database behind FreeRADIUS, including high availability and the independent scaling of RADIUS service layer and database layer. It includes benchmark data as well as a case study from a major ISP assessing MySQL Cluster for this purpose.
- Deploying FreeRADIUS with the MySQL Cluster Database: a technical white paper which explains how to configure both MySQL Cluster and FreeRADIUS for different scales of production deployments.
As these networks grow, limitations can occur which add administrative overhead, inhibit flexible scaling and impact the timely synchronization of data across the AAA environment.
Tweet
Deploying MySQL Cluster over multiple hosts
This post builds upon the earlier article (Creating a simple Cluster on a single LINUX host) which explained how to install and run a Cluster where all of the nodes run on the same physical host.
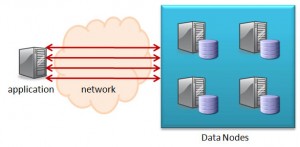
The single host solution is not great for a real deployment – MySQL Cluster is designed to provide a High Availability (HA) solution by synchronously replicating data between data nodes – if all of the data nodes run on a single host that that machine is a single point of failure.
This article demonstrates how to split the nodes between hosts; the configuration will still be fairly simple, using just 2 machines but it should be obvious how to extend it to more.
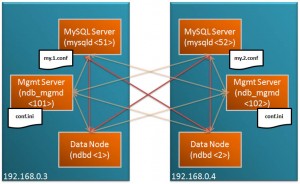
This new Cluster will be split across 2 machines, with all functions duplicated on each machine as shown in the diagram.
Downloading and installing
In the following example, host “ws1” has the IP Address 192.168.0.3 and “ws2” has 192.168.0.4.
Browse to the MySQL Cluster LINUX download page at mysql.com and download the correct version (32 or 64 bit) and store it in the desired directory (in my case, /home/billy/mysql) on both hosts and then extract and rename the new folder to something easier to work with…
[billy@ws1 mysql]$ tar xvf mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23.tar.gz [billy@ws1 mysql]$ mv mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23 7_0_6 [billy@ws2 mysql]$ tar xvf mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23.tar.gz [billy@ws2 mysql]$ mv mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23 7_0_6
Setup the files that will be needed for the MySQL Server processes (mysqld) to run correctly on each host…
[billy@ws1 mysql]$ cd 7_0_6 [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ scripts/mysql_install_db --basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6 --datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data [billy@ws2 mysql]$ cd 7_0_6 [billy@ws2 7_0_6]$ scripts/mysql_install_db --basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6 --datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data
Configure and run the Cluster
Create a sub-directory called “conf” on each host and create the following 3 files:
config.ini – note that this file is used by the management nodes and as we’re going to run an ndb_mgmd process on each host, this is created on both ws1 and ws2
[ndbd default] noofreplicas=2 [ndbd] hostname=192.168.0.3 id=1 [ndbd] hostname=192.168.0.4 id=2 [ndb_mgmd] id = 101 hostname=192.168.0.3 [ndb_mgmd] id = 102 hostname=192.168.0.4 [mysqld] id=51 hostname=192.168.0.3 [mysqld] id=52 hostname=192.168.0.4
my.1.conf – to be used by the MySQL Server on ws1 and so store on ws1
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=51
ndbcluster
datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data
basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6
port=3306
server-id=51
log-bin
my.2.conf – to be used by the MySQL Server on ws2 and so store on ws2
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=52
ndbcluster
datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data
basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6
port=3306
server-id=52
log-bin
Those files configure the nodes that make up the Cluster. From a command prompt window, launch the management nodes:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgmd --initial -f conf/config.ini --configdir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/conf [billy@ws2 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgmd --initial -f conf/config.ini --configdir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/conf
Check that the management nodes are up and running:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgm ndb_mgm> show Connected to Management Server at: localhost:1186 Cluster Configuration --------------------- [ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s) id=1 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.3) id=2 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.4) [ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 2 node(s) id=101 @192.168.0.3 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6) id=102 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.4) [mysqld(API)] 2 node(s) id=51 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.3) id=52 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.4) ndb_mgm> quit [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgm -c 192.168.0.4:1186 ndb_mgm> show Connected to Management Server at: 192.168.0.4:1186 Cluster Configuration --------------------- [ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s) id=1 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.3) id=2 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.4) [ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 2 node(s) id=101 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.3) id=102 @192.168.0.4 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6) [mysqld(API)] 2 node(s) id=51 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.3) id=52 (not connected, accepting connect from 192.168.0.4) ndb_mgm> quit
and then start the 2 data nodes (ndbd) and 2 MySQL API/Server nodes (mysqld) and then check that they’re all up and running:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndbd --initial -c localhost:1186
2009-06-17 13:05:47 [ndbd] INFO -- Configuration fetched from 'localhost:1186', generation: 1
[billy@ws2 7_0_6]$ bin/ndbd --initial -c localhost:1186
2009-06-17 13:05:51 [ndbd] INFO -- Configuration fetched from 'localhost:1186', generation: 1
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysqld --defaults-file=conf/my.1.conf&
[billy@ws2 7_0_6]$ bin/mysqld --defaults-file=conf/my.2.conf&
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgm
-- NDB Cluster -- Management Client --
ndb_mgm> show
Connected to Management Server at: localhost:1186
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=1 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0, Master)
id=2 @192.168.0.4 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 2 node(s)
id=101 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=102 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 2 node(s)
id=51 @192.168.0.3 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=52 @192.168.0.4 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
ndb_mgm> quit
Using the Cluster
There are now 2 API nodes/MySQL Servers/mysqlds running on the 2 different hosts; both accessing the same data. Each of those nodes can be accessed by the mysql client using the hostname and ports that were configured in the my.X.cnf files. For example, we can access the first of those nodes (node 51) in the following way (each API node is accessed using the host and port number in its associate my.X.cnf file:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -h localhost -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 4
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> create table assets (name varchar(30) not null primary key,
-> value int) engine=ndb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.99 sec)
mysql> insert into assets values ('Car','1900');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| Car | 1900 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
If you see “ERROR 1130 (HY000): Host ‘192.168.0.3’ is not allowed to connect to this MySQL server” then you need to set up the privileges (repeat on each host) – in a real system, you’d likely want tighter security that this:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -u root Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 3 Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL) Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO ''@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO ''@'192.168.0.4'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> quit Bye [billy@ws2 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -u root Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 8 Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL) Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO ''@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO ''@'192.168.0.3'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> quit Bye
Note that as this table is using the ndb (MySQL Cluster) storage engine, the data is actually held in the data nodes rather than in the SQL node and so we can access the exact same data from the the other SQL nodes:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -h 192.168.0.4 -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| Car | 1900 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
Your next steps
This is still a fairly simple, contrived set up. Hopefully it’s clear how additional data or SQL nodes could be added and in a larger deployment you may well decide to run the management and SQL nodes on different hosts to the data nodes (in fact, when starting up the management nodes there is a warning message suggesting you deploy them elsewhere!).
To move the management node to a 3rd, independent physical host (and a 4th one if you want 2 management nodes for redundancy -a future article will explain when you might want to do that), just change the IP address in the [ndb_mgmd] section of config.ini and then run the ndb_mgmd executable on that new host. Note that the management node consumes very few resources and so can share that host with other functions/applications (e.g. SQL Server nodes but not data nodes).
You’d also set several more variables in the configuration files in order to size and tune your Cluster.
In this article, I used 2 LINUX hosts but you could extend the Windows example introduced in My first Cluster running on Windows in exactly the same way.
Tweet
Intelligent user-controlled partitioning and writing distribution-aware NDB API Applications
Default partitioning
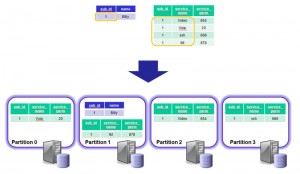
When adding rows to a table that’s using MySQL Cluster as the storage engine, each row is assigned to a partition where that partition is mastered by a particular data node in the Cluster. The best performance comes when all of the data required to satisfy a transaction is held within a single partition so that it can be satisfied within a single data node rather than being bounced back and forth between multiple nodes where extra latency will be introduced.
By default, Cluster partions the data by hashing the primary key. This is not always optimal.
For example, if we have 2 tables, the first using a single-column primary key (sub_id) and the second using a composite key (sub_id, service_name)…
mysql> describe names; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | sub_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(30) | YES | | NULL | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ mysql> describe services; +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | sub_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | 0 | | | service_name | varchar(30) | NO | PRI | | | | service_parm | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
If we then add data to these (initially empty) tables, we can then use the ‘explain’ command to see which partitions (and hence phyical hosts) are used to store the data for this single subscriber…
mysql> insert into names values (1,'Billy'); mysql> insert into services values (1,'VoIP',20),(1,'Video',654),(1,'IM',878),(1,'ssh',666); mysql> explain partitions select * from names where sub_id=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | names | p3 | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ mysql> explain partitions select * from services where sub_id=1; +----+-------------+----------+-------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+----------+-------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | services | p0,p1,p2,p3 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 10 | | +----+-------------+----------+-------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+
The service records for the same subscriber (sub_id = 1) are split accross 4 diffent partitions (p0, p1, p2 & p3). This means that the query results in messages being passed backwards and forwards between the 4 different data nodes which cnsumes extra CPU time and incurs extra latency.
User-defined partitioning to the rescue
We can override the default behaviour by telling Cluster which fields should be fed into the hash algorithm. For our example, it’s reasonable to expect a transaction to access multiple records for the same subscriber (identified by their sub_id) and so the application will perform best if all of the rows for that sub_id are held in the same partition…
mysql> drop table services; mysql> create table services (sub_id int, service_name varchar (30), service_parm int, primary key (sub_id, service_name)) engine = ndb -> partition by key (sub_id); mysql> insert into services values (1,'VoIP',20),(1,'Video',654),(1,'IM',878),(1,'ssh',666); mysql> explain partitions select * from services where sub_id=1; +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | services | p3 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 10 | | +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+
Now all of the rows for sub_id=1 from the services table are now held within a single partition (p3) which is the same as that holding the row for the same sub_id in the names table. Note that it wasn’t necessary to drop, recreate and re-provision the services table, the following command would have had the same effect:
mysql> alter table services partition by key (sub_id);
Writing a distribution-aware application using the NDB API
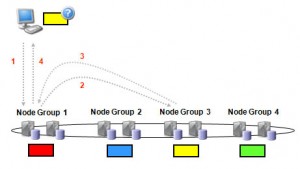
In our example, the data is nicely partitioned for optimum performance when accessing all of the subscriber’s data – a single data node holding all of their data. However, there is another step to take to get the best out of your NDB-API based application. By default, the NDB API will use the Transaction Coordinator (TC) on a ‘random’ data node to handle the transaction – we could get lucky and the guess is correct but it’s more likely that it will be sent to the wrong data node which with then have to proxy it to the correct data node. The probability of getting it right first time reduces as the number of node groups increases and so can prevent linear scaling.
It’s very simple to modify this behaviour so that the best data node/TC is hit first time, every time. When creating the transaction, the application can include parameters telling the NDB API one of the tables to be accessed and for what key(s). The NDB API will then use that information to identify the best TC to use…
const NdbDictionary::Dictionary* myDict= myNdb.getDictionary();
const NdbDictionary::Table *namesTable= myDict->getTable("names");
const NdbDictionary::Table *servicesTable= myDict->getTable("services");
NdbRecAttr *myRecAttr;
Ndb::Key_part_ptr dist_key[2];
dist_key[0].ptr = (const void*) &sub_id;
dist_key[0].len = sizeof(sub_id);
dist_key[1].ptr = NULL;
dist_key[1].len = NULL;
if (namesTable == NULL)
APIERROR(myDict->getNdbError());
if (servicesTable == NULL)
APIERROR(myDict->getNdbError());
NdbTransaction *myTransaction= myNdb.startTransaction(namesTable,
dist_key);
if (myTransaction == NULL) APIERROR(myNdb.getNdbError());
NdbOperation *myOperation= myTransaction->getNdbOperation(namesTable);
if (myOperation == NULL) APIERROR(myTransaction->getNdbError());
myOperation->readTuple(NdbOperation::LM_Read);
myOperation->equal("sub_id",sub_id);
myRecAttr= myOperation->getValue("name", NULL);
if (myRecAttr == NULL) APIERROR(myTransaction->getNdbError());
// Perform operations on "services" table as well as part of another operation
// if required; the subscriber's data will be in the same data node
if (myTransaction->execute( NdbTransaction::Commit ) == -1)
APIERROR(myTransaction->getNdbError());
printf(" %2d %sn",
sub_id, myRecAttr->aRef());
myNdb.closeTransaction(myTransaction);
Note that as the services table has been configured to use the same field (sub_id) for partitioning as the names table, the startTransaction method only needs to know about the namesTable as the TC that the NDB API selects will serve just as well for this subscriber’s data from the services table. The rest of the code can be found in distaware.
Tweet
MySQL Cluster Multi-Range Read using NDB API
As described in “Batching – improving MySQL Cluster performance when using the NDB API“, reducing the number of times the application node has to access the data nodes can greatly improve performance and reduce latency. That article focussed on setting up multiple operatations (as part of a single transaction) and then executing them as a single batch sent by the NDB API library to the data nodes.
The purpose of this entry is to show how a single NDB API operation can access multiple rows from a table with a single index lookup. It goes on to explain the signifficance of this both now and in the future (much faster joins using SQL for MySQL Cluster tables).
There are several operation types to cover table scans and index lookups (refer to the “MySQL Cluster API Developer Guide” for detals). For this example, I use an NdbIndexScanOperation.
The code sample assumes that the following table structure and data has been set up for table “COUNTRY” in database “TEST_DB_1” using the NDB storage engine (Note that the full example application sets this up automatically):
+--------------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | SUB_ID | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | | | COUNTRY_CODE | int(10) unsigned | NO | | NULL | | +--------------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ +--------+--------------+ | SUB_ID | COUNTRY_CODE | +--------+--------------+ | 13 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | | 4 | 61 | | 7 | 46 | | 9 | 44 | | 10 | 33 | | 12 | 44 | | 5 | 33 | | 14 | 61 | | 1 | 44 | | 8 | 1 | +--------+--------------+
The following code causes the NDB API library to send a single request from the application to the data nodes to read the rows where the primary key “SUB_ID” falls into the ranges (2<= SUB_ID <4); (5 < SUB_ID <=9) or (SUB_ID == 13). Note that this is just a fragment of the code and the error checking has been removed for clarity (refer to full example application to see the rest of the code, including the error handling).
NdbIndexScanOperation *psop;
/* RecAttrs for NdbRecAttr Api */
NdbRecAttr *recAttrAttr1;
NdbRecAttr *recAttrAttr2;
psop=myTransaction->getNdbIndexScanOperation(myPIndex);
Uint32 scanFlags=
NdbScanOperation::SF_OrderBy |
NdbScanOperation::SF_MultiRange |
NdbScanOperation::SF_ReadRangeNo;
psop->readTuples(NdbOperation::LM_Read,
scanFlags,
(Uint32) 0, // batch
(Uint32) 0) // parallel
/* Add a bound
* Tuples where SUB_ID >=2 and < 4
*/
Uint32 low=2;
Uint32 high=4;
Uint32 match=13;
psop->setBound("SUB_ID", NdbIndexScanOperation::BoundLE, (char*)&low);
psop->setBound("SUB_ID", NdbIndexScanOperation::BoundGT, (char*)&high);
psop->end_of_bound(0);
/* Second bound
* Tuples where SUB_ID > 5 and <=9
*/
low=5;
high=9;
psop->setBound("SUB_ID", NdbIndexScanOperation::BoundLT, (char*)&low);
psop->setBound("SUB_ID", NdbIndexScanOperation::BoundGE, (char*)&high);
psop->end_of_bound(1);
/* Third bound
* Tuples where SUB_ID == 13
*/
psop->setBound("SUB_ID", NdbIndexScanOperation::BoundEQ, (char*)&match);
psop->end_of_bound(2);
/* Read all columns */
recAttrAttr1=psop->getValue("SUB_ID");
recAttrAttr2=psop->getValue("COUNTRY_CODE");
myTransaction->execute( NdbTransaction::Commit);
while (psop->nextResult(true) == 0)
{
printf(" %8d %8d Range no : %2dn",
recAttrAttr1->u_32_value(),
recAttrAttr2->u_32_value(),
psop->get_range_no());
}
psop->close();
When run, this code produces the following output:
SUB_ID COUNTRY_CODE 2 1 Range no : 0 7 46 Range no : 1 8 1 Range no : 1 9 44 Range no : 1 13 1 Range no : 2
Why is this signifficant?
This can be very useful for applications using the NDB API; imagine an application that wanted to find the birthdays for all of my friends. Assume that I have 2 tables of interest:
mysql> describe friends; describe birthday; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | name | varchar(30) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | friend | varchar(30) | NO | PRI | | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | name | varchar(30) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | day | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | month | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | year | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Using the NDB API, I can create 1 NdbIndexScanOperation operation to read all tuples from “friends” where the “name” field matches “Andrew” and then use the results to perform a second NdbIndexScanOperation to read the rows that match each of my friends’ names in the “birthday” table. In other words, performing a join using only 2 trips from the application to the data nodes.
Of course, it’s simple to get the same results using SQL…SELECT birthday.name, birthday.day, birthday.month FROM friends, birthday WHERE friend.name='Andrew' AND friends.friend=birthday.name;However, if the tables are very large and I have a lot of friends then performing this join using SQL can be expensive as it requires a separate trip to the data nodes to fetch each birthday. In the future, Batched Key Access (BKA) will optimise these joins by performing one of these NDB API Multi-Range Reads (MRR) to fetch all of the birthdays in one go! Until then, using the NDB API directly can deliver signifficantly faster results.
Tweet
Batching – improving MySQL Cluster performance when using the NDB API
As many people are aware, the best performance can be achieved from MySQL Cluster by using the native (C++) NDB API (rather than using SQL via a MySQL Server). What’s less well known is that you can improve the performance of your NDB-API enabled application even further by ‘batching’. This article attempts to explain why batching helps and how to do it.
What is batching and why does it help?
Batching involves sending multiple operations from the application to the Cluster in one group rather than individually; the Cluster then processes these operations and sends back the results. Without batching, each of these operations incurs the latency of crossing the network as well as consuming CPU time on both the application and data node hosts.
By batching together multiple operations, all of the requests can be sent in one message and all of the replies received in another – thus reducing the number of messages and hence the latency and CPU time consumed.
How to use batching with the MySQL Cluster NDB API
The principle is that you batch together as many operations as you can, execute them together and then interpret the results. After interpretting the results, the application may then decide to send in another batch of operations.
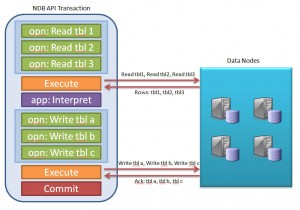
An NDB API transaction consists of one or more operations where each operation (currently) acts on a single table and could be a simple primary key read or write or a complex table scan.
The operation is not sent to the Cluster at the point that it’s defined. Instead, the application must explicitly request that all operations defined within the transaction up to that point be executed – at which point, the NDB API can send the batch of operations to the data nodes to be processed. The application may request that the transaction be committed at that point or it may ask for the transaction to be held open so that it can analyse the results from the first set of operations and then use that information within a subsequent series of operations and then commit the transaction after executing that second batch of operations.
The following code sample shows how this can be implemented in practice (note that the application logic and all error handling has been ommited).
const NdbDictionary::Dictionary* myDict= myNdb.getDictionary();
const NdbDictionary::Table *myTable= myDict->getTable("tbl1");
const NdbDictionary::Table *myTable2= myDict->getTable("tbl2");
NdbTransaction *myTransaction= myNdb.startTransaction();
// Read all of the required data as part of a single batch
NdbOperation *myOperation= myTransaction->getNdbOperation(myTable1);
myOperation->readTuple(NdbOperation::LM_Read);
myOperation->equal("ref", asset_num);
myRecAttr= myOperation->getValue("cost", NULL);
NdbOperation *myOperation2= myTransaction->getNdbOperation(myTable2);
myOperation2->readTuple(NdbOperation::LM_Read);
myOperation2->equal("ref", asset_num);
myRecAttr= myOperation->getValue("volume", NULL);
myTransaction->execute(NdbTransaction::NoCommit);
// NOT SHOWN: Application logic interprets results from first set of operations
// Based on the data read during the initial batch, make the necessary changes
myOperation *myOperation3= myTransaction->getNdbOperation(myTable1);
myOperation3->updateTuple();
myOperation3->equal("ref", asset_num);
myOperation2->setValue("cost", new_cost);
myOperation *myOperation4= myTransaction->getNdbOperation(myTable2);
myOperation4->updateTuple();
myOperation4->equal("ref", asset_num);
myOperation4->setValue("volume", new_volume);
myTransaction->execute( NdbTransaction::Commit);
myNdb.closeTransaction(myTransaction);
Tweet
Upcoming Webinar: Guide to Scaling OpenLDAP: MySQL Cluster as Data Store for OpenLDAP Directories
From MySQL Cluster 7.0, it’s possible to use Cluster as the Data Store for the OpenLDAP Directory Server – this has 2 very signifficant implications:
- All of the advantages of MySQL Cluster (scalability, high availability and cost) can now be applied to your directory server deployment
- The same data held in a MySQL Cluster database can now be accessed simultaneously using LDAP in addition to SQL, the native C++ interface and all of the connectors available for MySQL
Howard Chu (Chief Architect of the OpenLDAP project and CTO of Symas) will be presenting a Webinar on Wednesday together with Mat Keep from MySQL. I’ll be helping with the Q&A.
Webinar details…
Wednesday, June 24, 2009
Discover how to fully exploit distributed subscriber and network data, and how to enhance your investments in OpenLDAP technology by tuning into this webinar, jointly run by OpenLDAP and MySQL.
In this webinar, the Chief Architect of OpenLDAP will demonstrate where this solution can be used, and how to get started with MySQL Cluster as the directory data store.
MySQL Cluster has been widely deployed for subscriber databases within Communications Service Provider networks. Extending this capability, MySQL Cluster Carrier Grade Edition 7.0 can be deployed as the back-end data store for LDAP directory servers.
Using industry standard LDAP directories with MySQL Cluster serving as the directory data store, operators can leverage standard LDAP interfaces to consolidate data stores, and for the authentication and authorization of devices and subscribers with real-time performance and carrier-grade availability requirements. The result is total solution that reduces cost, risk and complexity for large, transaction-intensive directory data sets.
WHEN:
Wednesday, June 24, 2009: 10:00 Pacific time (America)
Wed, Jun 24: 07:00 Hawaii time
Wed, Jun 24: 11:00 Mountain time (America)
Wed, Jun 24: 12:00 Central time (America)
Wed, Jun 24: 13:00 Eastern time (America)
Wed, Jun 24: 17:00 UTC
Wed, Jun 24: 18:00 Western European time
Wed, Jun 24: 19:00 Central European time
Wed, Jun 24: 20:00 Eastern European time
The presentation will be approximately 45 minutes long followed by Q&A.
Tweet
Creating a simple Cluster on a single LINUX host
It isn’t necessarily immediately obvious how to set up a Cluster on LINUX; this post attempts to show how to get a simple Cluster up and running. For simplicity, all of the nodes will run on a single host – a subsequent post will take the subsequent steps of moving some of them to a second host. As with my Windows post the Cluster will contain the following nodes:
- 1 Management node (ndb_mgmd)
- 2 Data nodes (ndbd)
- 3 MySQL Server (API) nodes (mysqld)
Downloading and installing
Browse to the MySQL Cluster LINUX download page at mysql.com and download the correct version (32 or 64 bit) and store it in the desired directory (in my case, /home/billy/mysql) and then extract and rename the new folder to something easier to work with…
[billy@ws1 mysql]$ tar xvf mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23.tar.gz
[billy@ws1 mysql]$ mv mysql-cluster-gpl-7.0.6-linux-x86_64-glibc23 7_0_6
Create 3 data folders (one for each of the MySQL API – mysqld – processes) and setup the files that will be needed for them to run correctly…
[billy@ws1 mysql]$ cd 7_0_6/data [billy@ws1 data]$ mkdir data1 data2 data3 [billy@ws1 data]$ mkdir data1/mysql data1/test data2/mysql data2/test data3/mysql data3/test [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ cd .. [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ scripts/mysql_install_db --basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6 --datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data1 [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ scripts/mysql_install_db --basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6 --datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data2 [billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ scripts/mysql_install_db --basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6 --datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data3
Configure and run the Cluster
Create a sub-directory called “conf” and create the following 4 files there:
config.ini
[ndbd default]
noofreplicas=2
[ndbd]
hostname=localhost
id=2
[ndbd]
hostname=localhost
id=3
[ndb_mgmd]
id = 1
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=4
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=5
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=6
hostname=localhost
my.1.conf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=4
ndbcluster
datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data1
basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6
port=3306
server-id=1
log-bin
my.2.conf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=5
ndbcluster
datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data2
basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6
port=3307
server-id=2
log-bin
my.3.conf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=6
ndbcluster
datadir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/data/data3
basedir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6
port=3308
server-id=3
log-bin
Those files configure the nodes that make up the Cluster. From a command prompt window, launch the management node:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgmd --initial -f conf/config.ini --configdir=/home/billy/mysql/7_0_6/conf 2009-06-17 13:00:08 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- NDB Cluster Management Server. mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6 2009-06-17 13:00:08 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- Reading cluster configuration from 'conf/config.ini'
Check that the management node is up and running:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgm
ndb_mgm> show
Connected to Management Server at: localhost:1186
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=3 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @localhost (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 3 node(s)
id=4 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=5 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=6 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
ndb_mgm> quit
and then start the 2 data nodes (ndbd) and 3 MySQL API/Server nodes (ndbd) and then check that they’re all up and running:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndbd --initial -c localhost:1186
2009-06-17 13:05:47 [ndbd] INFO -- Configuration fetched from 'localhost:1186', generation: 1
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndbd --initial -c localhost:1186
2009-06-17 13:05:51 [ndbd] INFO -- Configuration fetched from 'localhost:1186', generation: 1
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysqld --defaults-file=conf/my.1.conf&
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysqld --defaults-file=conf/my.2.conf&
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysqld --defaults-file=conf/my.3.conf&
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/ndb_mgm
-- NDB Cluster -- Management Client --
ndb_mgm> show
Connected to Management Server at: localhost:1186
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0, Master)
id=3 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 3 node(s)
id=4 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=5 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=6 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
ndb_mgm> quit
Using the Cluster
There are now 3 API nodes/MySQL Servers/mysqlds running; all accessing the same data. Each of those nodes can be accessed by the mysql client using the ports that were configured in the my.X.cnf files. For example, we can access the first of those nodes (node 4) in the following way (each API node is accessed using the port number in its associate my.X.cnf file:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -h localhost -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 4
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> create table assets (name varchar(30) not null primary key,
-> value int) engine=ndb;
090617 13:21:36 [Note] NDB Binlog: CREATE TABLE Event: REPL$test/assets
090617 13:21:36 [Note] NDB Binlog: logging ./test/assets (UPDATED,USE_WRITE)
090617 13:21:37 [Note] NDB Binlog: DISCOVER TABLE Event: REPL$test/assets
090617 13:21:37 [Note] NDB Binlog: DISCOVER TABLE Event: REPL$test/assets
090617 13:21:37 [Note] NDB Binlog: logging ./test/assets (UPDATED,USE_WRITE)
090617 13:21:37 [Note] NDB Binlog: logging ./test/assets (UPDATED,USE_WRITE)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.99 sec)
mysql> insert into assets values ('Car','1900');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| Car | 1900 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
Note that as this table is using the ndb (MySQL Cluster) storage engine, the data is actually held in the data nodes rather than in the SQL node and so we can access the exact same data from either of the other 2 SQL nodes:
[billy@ws1 7_0_6]$ bin/mysql -h localhost -P 3307
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 5
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl-log MySQL Cluster Server (GPL)
type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| Car | 1900 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
Your next steps
This is a very simple, contrived set up – in any sensible deployment, the nodes would be spread across multiple physical hosts in the interests of performance and redundancy (take a look at the new article (Deploying MySQL Cluster over multiple host) to see how to do that). You’d also set several more variables in the configuration files in order to size and tune your Cluster.
Tweet
My first Cluster running on Windows
I figured that it was time to check out how to install, configure, run and use MySQL Cluster on Windows. To keep things simple, this first Cluster will all run on a single host but includes these nodes:
- 1 Management node (ndb_mgmd)
- 2 Data nodes (ndbd)
- 3 MySQL Server (API) nodes (mysqld)
Downloading and installing
Browse to the Windows section of the MySQL Cluster 7.0 download page and download the installer (32 or 64 bit).
Run the .msi file and choose the “Custom” option. Don’t worry about the fact that it’s branded as “MySQL Server 7.0” and that you’ll go on to see adverts for MySQL Enterprise – that’s just an artefact of how the installer was put together.
On the next screen, I decided to change the “Install to” directory to “c:mysql” – not essential but it saves some typing later.
Go ahead and install the software and then you’ll be asked if you want to configure the server – uncheck that as we’ll want to tailor the configuration so that it works with our Cluster.
There are a couple of changes you need to make to your Windows configuration before going any further:
- Add the new bin folder to your path (in my case “C:mysqlbin”)
- Make hidden files visible (needed in order to set up multiple MySQL Server processes on the same machine)
Configure and run the Cluster
Copy the contents of “C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data” to “C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data4”, “C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data5” and “C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data6”. Note that this assumes that you’ve already made hidden files visible. Each of these folders will be used by one of the mysqld processes.
Create the folder “c:mysqlcluster” and then create the following files there:
config.ini
[ndbd default]
noofreplicas=2
[ndbd]
hostname=localhost
id=2
[ndbd]
hostname=localhost
id=3
[ndb_mgmd]
id = 1
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=4
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=5
hostname=localhost
[mysqld]
id=6
hostname=localhost
my.4.cnf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=4
ndbcluster
datadir="C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data4"
port=3306
server-id=3306
my.5.cnf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=5
ndbcluster
datadir="C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data5"
port=3307
server-id=3307
my.6.cnf
[mysqld]
ndb-nodeid=6
ndbcluster
datadir="C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 7.0data6"
port=3308
server-id=3308
Those files configure the nodes that make up the Cluster.
From a command prompt window, launch the management node:
C:UsersAndrew>cd mysqlcluster
C:mysqlcluster>ndb_mgmd -f config.ini
2009-06-16 20:01:20 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- NDB Cluster Management Server. mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6
2009-06-16 20:01:20 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- The default config directory 'c:mysqlmysql-cluster' does not exist. Trying to create it...
2009-06-16 20:01:20 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- Sucessfully created config directory
2009-06-16 20:01:20 [MgmSrvr] INFO -- Reading cluster configuration from 'config.ini'
and then from another window, check that the cluster has been defined:
C:UsersAndrew>ndb_mgm
-- NDB Cluster -- Management Client --
ndb_mgm> show
Connected to Management Server at: localhost:1186
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=3 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @localhost (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 3 node(s)
id=4 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=5 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=6 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
Fire up 2 more command prompt windows and launch the 2 data nodes:
C:UsersAndrew>ndbd
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- Configuration fetched from 'localhost:118
6', generation: 1
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- Ndb started
NDBMT: non-mt
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- NDB Cluster -- DB node 2
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6 --
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- Ndbd_mem_manager::init(1) min: 84Mb initi
al: 104Mb
Adding 104Mb to ZONE_LO (1,3327)
2009-06-16 20:08:57 [ndbd] INFO -- Start initiated (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
WOPool::init(61, 9)
RWPool::init(22, 13)
RWPool::init(42, 18)
RWPool::init(62, 13)
Using 1 fragments per node
RWPool::init(c2, 18)
RWPool::init(e2, 14)
WOPool::init(41, 8 )
RWPool::init(82, 12)
RWPool::init(a2, 52)
WOPool::init(21, 5)
(repeat from another new window for the second data node).
After both data nodes (ndbd) have been launched, you should be able to see them through the management client:
ndb_mgm> show
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0, Master)
id=3 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 3 node(s)
id=4 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=5 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
id=6 (not connected, accepting connect from localhost)
Finally, the 3 MySQL Server/API nodes should be lauched from 3 new windows:
C:UsersAndrew>cd mysqlcluster
C:mysqlcluster>mysqld --defaults-file=my.4.cnf
C:UsersAndrew>cd mysqlcluster
C:mysqlcluster>mysqld --defaults-file=my.5.cnf
C:UsersAndrew>cd mysqlcluster
C:mysqlcluster>mysqld --defaults-file=my.6.cnf
Now, just check that all of the Cluster nodes are now up and running from the management client…
ndb_mgm> show
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0, Master)
id=3 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6, Nodegroup: 0)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
[mysqld(API)] 3 node(s)
id=4 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=5 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
id=6 @127.0.0.1 (mysql-5.1.34 ndb-7.0.6)
Using the Cluster
There are now 3 API nodes/MySQL Servers/mgmds running; all accessing the same data. Each of those nodes can be accessed by the mysql client using the ports that were configured in the my.X.cnf files. For example, we can access the first of those nodes (node 4) in the following way from (yet another) window:
C:UsersAndrew>mysql -h localhost -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl MySQL Cluster Server (GPLType 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> create table assets (name varchar(30) not null primary key, value int) engine=ndb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.44 sec
mysql> insert into assets values ('car', 950);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| car | 950 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec
mysql> insert into assets2 values ('car', 950);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
To check that everything is working correctly, we can access the same database through another of the API nodes:
C:UsersAndrew>mysql -h localhost -P 3307
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.1.34-ndb-7.0.6-cluster-gpl MySQL Cluster Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| assets |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
mysql> select * from assets;
+------+-------+
| name | value |
+------+-------+
| car | 950 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.09 sec)
It’s important to note that the table (and its contents) of any table created using the ndb storage engine can be accessed through any of the API nodes but those created using other storage engines are local to each of the API nodes (MySQL Servers).
Your next steps
This is a very simple, contrived set up – in any sensible deployment, the nodes would be spread accross multiple physical hosts in the interests of performance and redundancy. You’d also set several more variables in the configuration files in order to size and tune your Cluster. Finally, you’d likely want to have some of these processes running as daemons or services rather than firing up so many windows.
It’s important to note that Windows is not a fully supported platform for MySQL Cluster. If you have an interest in deploying a production system on Windows then please contact me at andrew@clusterdb.com
Tweet
MySQL Cluster – flexibility of replication
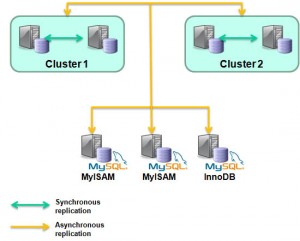
One of the better kept secrets about MySQL Cluster appears to be the flexibility available when setting up replication. Rather than being constrained to implementing a single replication scheme, you can mix and match approaches.
Just about every Cluster deployment will use synchronous replication between the data nodes within a node group to implement High Availability (HA) by making sure that at the point a transaction is committed, the new data is stored in at least 2 physical hosts. Given that MySQL Cluster is usually used to store the data in main memory rather than on disk, this is pretty much mandatory (note that the data changes are still written to disk but that’s done asynchronously to avoid slowing down the database).
MySQL asynchronous replication is often used for MySQL Cluster deployments in order to provide Geographic Redundancy. At the same time as the synchronous replication within a Cluster, the changes can be replicated asynchronously to a second Cluster (or to more than one) at a remote location. Asynchronous rather than synchronous replication is used so that the transaction commit is not delayed while waiting for the remote (could be thousands of miles away, connected by a high latency WAN) Cluster to receive, apply and acknowledge the change. A common misconception is that changes being made through the NDB API will not be replicated to the remote site as this replication is handled by a MySQL Server instance – the reality is that the MySQL Replication implementation will pick up the changes even when they’re written directly to the data nodes through the NDB API.
A third use of replication is to store the Cluster’s data in a seperate database – for example to have a read-only, up-to-date copy of the data stored within the MyISAM storage engine so that complex reports can be generated from it. And the best news is that this can be done at the same time as the local HA and remote Geographic Redundancy replication!
Johan’s Blog provides the technical details around configuring replication in order to provide some extra scaling by setting up non-Cluster slave databases that pick up all changes from the Cluster database.
Tweet